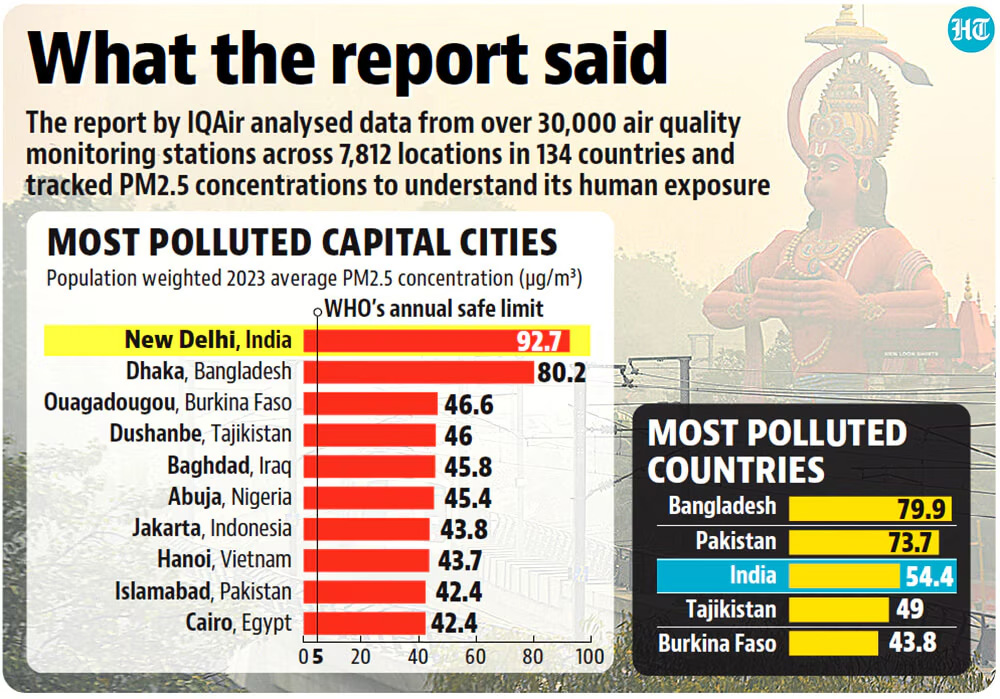
New Delhi: In 2023, New Delhi earned the ignominious title of the world’s most polluted capital city, with residents enduring air quality nearly 20 times higher than the international safe standard. Data from Swiss firm IQAir, released on Tuesday, further ranked India as the third most polluted country globally.
In 2023, New Delhi surpassed Dhaka to become the world’s most polluted capital city, with an annual population-weighted PM2.5 of 92.7µg/m3, nearly 20 times the international safe standard. Burkina Faso’s capital, Ouagadougou, ranked third with a distant PM2.5 of 46.6µg/m3.
Of the 50 most polluted cities globally, 42 were in India, up from 39 in 2022, with Begusarai in Bihar topping the list at 118.9µg/m3, followed by Guwahati at 105.4µg/m3.
New Delhi, both as the larger Union territory and as the smaller capital, ranked third and sixth respectively globally, with PM2.5 concentrations of 102.1µg/m3 and 46.6µg/m3.
In the National Capital Region (NCR), Greater Noida and Gurugram ranked as the most polluted cities globally, with PM2.5 concentrations of 88.6µg/m3 and 84µg/m3 respectively.
The findings were part of the World Air Quality Report 2023, reflecting the annual challenge of air pollution during the Diwali season and throughout the winter in the NCR.
Over the past decade, central and state governments have implemented measures to combat pollution, including the Graded Response Action Plan (Grap) and the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) for NCR.
Exposure to PM2.5 pollution can exacerbate various health conditions and impair cognitive development, particularly in children. Factors contributing to Delhi’s pollution include vehicle emissions, crop burning, and industrial and biomass burning.
India ranked third globally in PM2.5 pollution, with an annual average of 54.4µg/m3, trailing behind Pakistan and Bangladesh. However, efforts to address pollution have shown some improvement in certain regions.
The report highlighted the need for urgent action to monitor air quality, manage transboundary haze, and reduce reliance on combustion as an energy source to mitigate the global health crisis posed by air pollution.

